Table of Contents
Java 8 Features⌗
- Functional Interfaces
- Methods
- Streams
- Date and Time
Why Java 8 is Important?⌗
- java 8 improves overall application performance with little work.
- Lambda Expressions, Stream API, new methods added to existing classes improve productivity.
- Java 8 Optional type gives developers flexibility when dealing with null values, reducing the likelihood of NullPointerExceptions.
- Less Code: Java 8 reduces boilerplate with a functional style, focusing on what to do, not how.
- Parallel Friendly: With simple APIs, the JVM splits tasks and runs them across cores using fork/join.
Reactive Programming⌗
- It’s a design pattern that focuses on use of asynchronous and non-blocking data streams to handle data and events.
Need of Reactive Programming⌗
- For Efficiency and Scalability.
Without Reactive Programming⌗
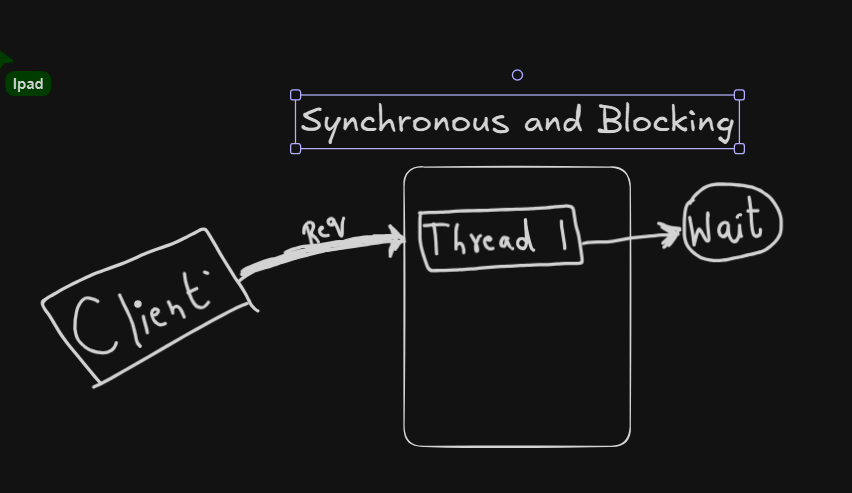 \ Thread will be blocked until Operation is done.
\ Thread will be blocked until Operation is done.
With Reactive Programming⌗
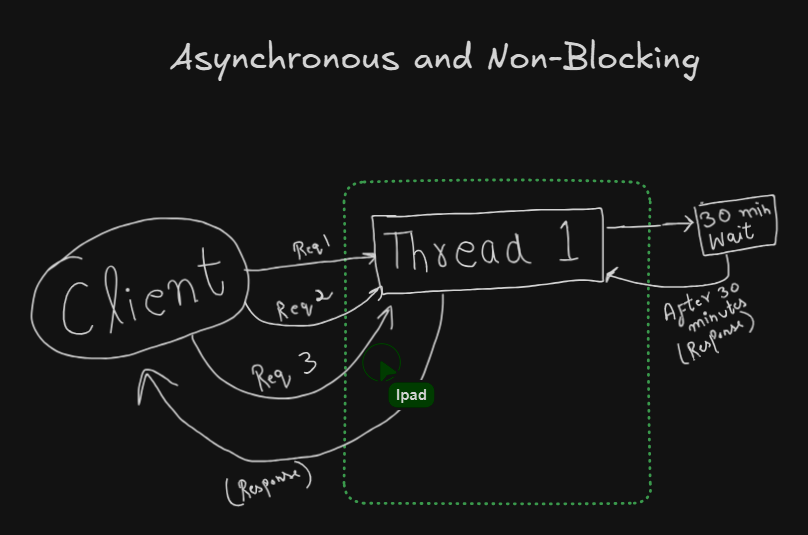 Thread don’t wait for Response.
Thread don’t wait for Response.
Functional Interface⌗
A functional interface in Java is an interface that contains exactly one abstract method. It can have any number of default or static methods, but only one abstract method.
Lambda Expressions⌗
A lambda expression is a concise way to represent an anonymous function—a function without a name—in Java. Introduced in Java 8.
Comparable<> Interface⌗
The Comparable<T> interface is used to define the natural ordering of objects.
It allows a class to compare its instances using the compareTo() method.
✅ Syntax Example:⌗
class Student implements Comparable<Student> {
int rollNo;
public int compareTo(Student other) {
return this.rollNo - other.rollNo;
}
}
✅ What does this mean in compareTo()?⌗
-
this→ current object (e.g.,s1) -
other→ object passed for comparison (e.g.,s2) -
this.rollNo - other.rollNo:-
Negative →
thiscomes before -
Zero → equal
-
Positive →
thiscomes after
-
✅ What does Collections.sort(students) do?⌗
-
Sorts the list using the logic in
compareTo(). -
Internally calls:
java
CopyEdit
s1.compareTo(s2)for every pair of objects.
✅ When to use Comparable?⌗
-
When the class should define its own default sorting rule (e.g., by roll number, name, etc.).
-
Works automatically with
Collections.sort()orArrays.sort().