B-Tree
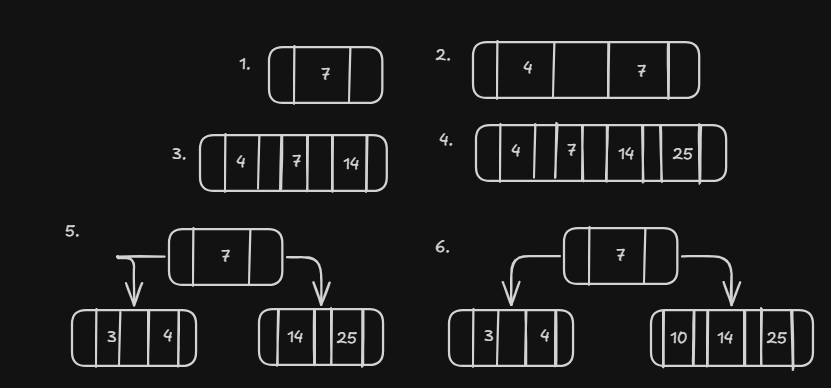
🌳 B-Tree Nomenclature
- Order (m) → max children =
m - Max keys →
m − 1 - Min keys (non-root) →
⌈m/2⌉ − 1 - Children vs Keys →
keys = children − 1 - Root → minimum
1key - Internal node → has children
- Leaf node → no children
- All leaves → same level (balanced)
- Height →
O(logₘ n)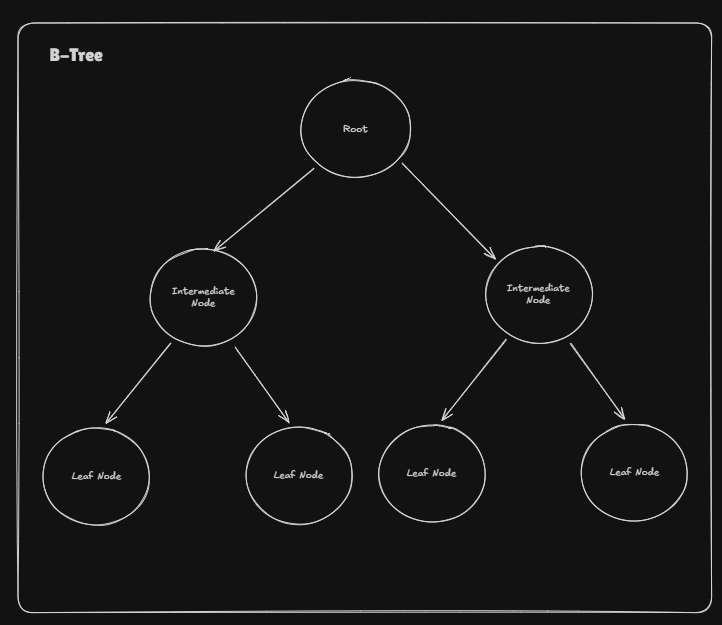
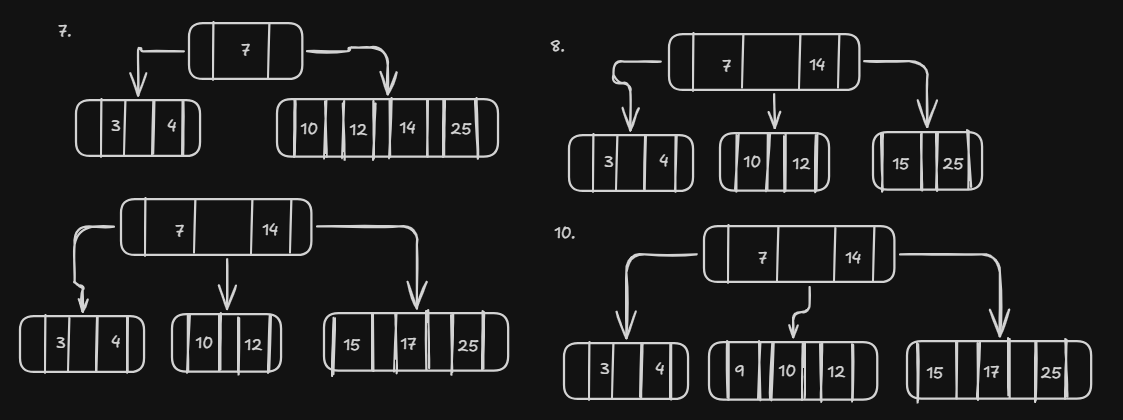
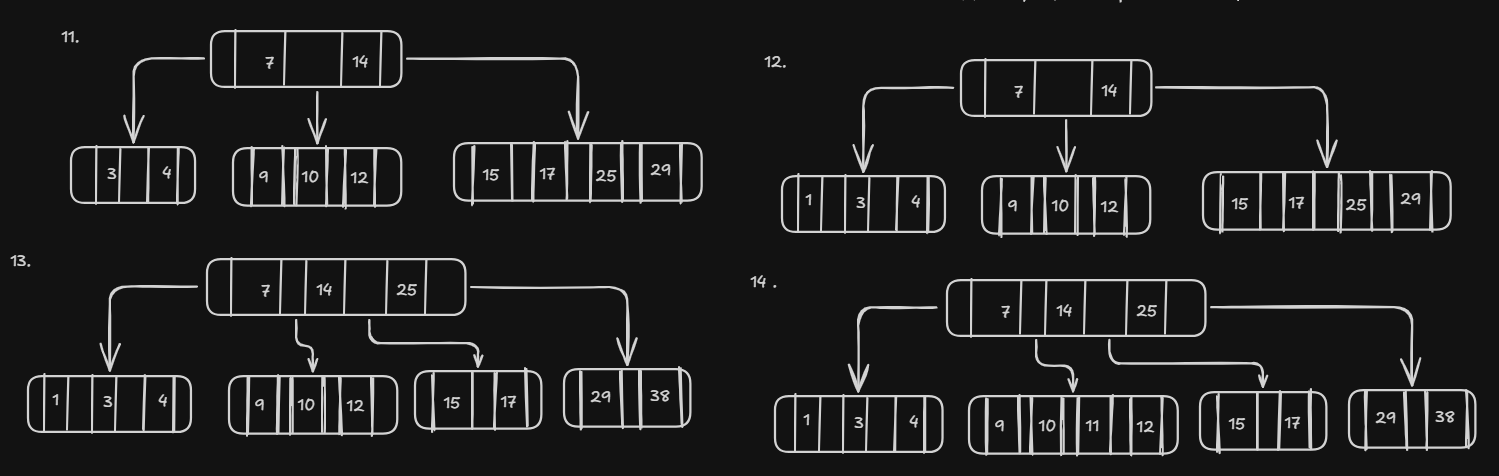
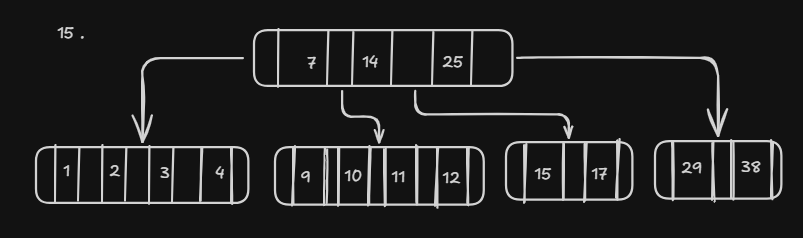
Insert Operation
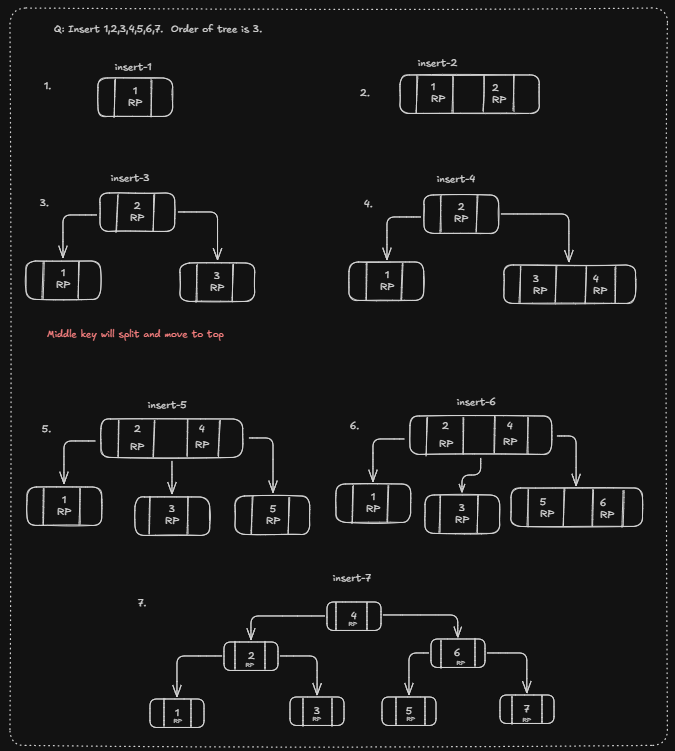
Insert Operation another example
B-Tree of Order 5
Insert Keys 7, 4, 14, 25, 3, 10, 12, 15, 17, 9, 29, 1, 38, 2, 11